ON THIS PAGE: You will find drawings of the main body parts affected by astrocytoma. Use the menu to see other pages.
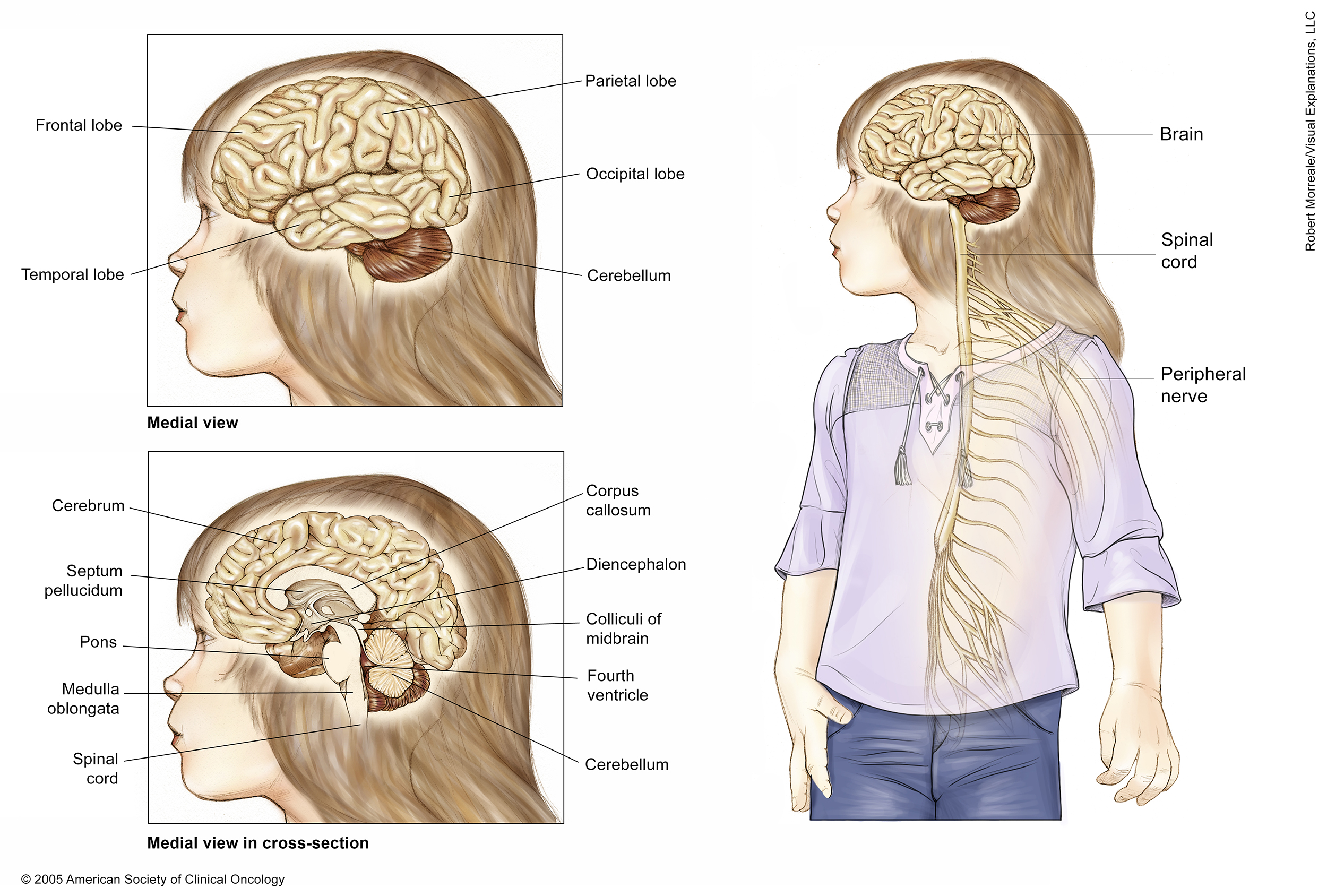

These illustrations show several views of a child’s brain and central nervous system. A medial (side) view of the brain shows the cerebrum and cerebellum. The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and made up of 4 lobes: the frontal lobe at the front of the skull, the parietal lobe at the upper rear of the skull (above the occipital lobe), and the temporal lobe, which is located under the frontal and parietal lobes on both sides of the cerebrum. The cerebellum is located under the occipital and temporal lobes at the rear of the skull.
The cross section of the brain shows the long corpus callosum located under the cerebrum in the center of the brain, the septum pellucidum, which runs down from the corpus callosum, and the diencephalon, which connects the cerebrum and the brain stem. The brain stem is the lowest part of the brain. It is made up of 3 parts: the medulla oblongata, which connects to the spinal cord; the pons, which bulges out from the medulla oblongata; and the midbrain. The fourth ventricle is a fluid-filled space between the brain stem and the cerebellum, underneath the colliculi of the midbrain.
An overall view of the body shows that the spinal cord extends from the brain stem down the back. Peripheral nerves branch out from the spinal cord to the rest of the body.
Copyright 2004 American Society of Clinical Oncology. Robert Morreale/Visual Explanations, LLC.
The next section in this guide is Risk Factors. It describes the factors that may increase the chance of developing astrocytoma. Use the menu to choose a different section to read in this guide.
